7.1. Overview¶
The OmniSciDB Query Engine refers to the system components which manage query kernel compilation and kernel execution. The RelAlgExecutor manages overall query state, while the Executor manages the code generation and execution for each query step. A query step takes as input a WorkUnit and returns a ResultSet. The query engine includes support for complex, multi-step queries (e.g. joins on subquery results) as well as code generation and execution for queries which can run on either the CPU or the GPU. The general execution sequence for a single relational algebra query is depicted below.
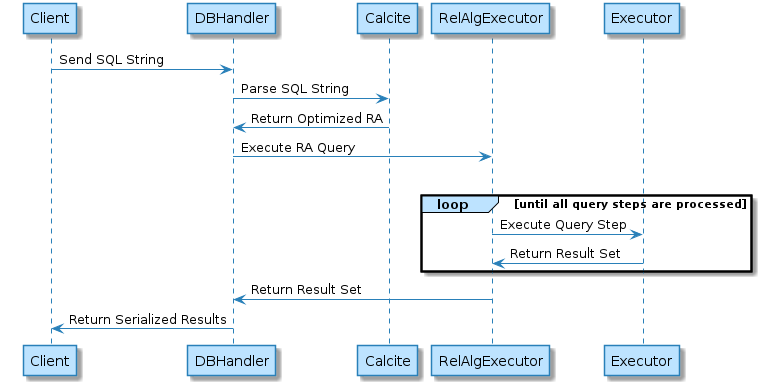
7.1.1. Request Handler (DBHandler)¶
The DBHandler class manages client interactions with the server. Clients initiate a SQL query by passing the query string and various parameters to the sql_execute endpoint. The handler manages the RelAlgExecutor for the duration of the query, passes the SQL string to Calcite for parsing and optimization, and handles serializing and returning results to the client.
7.1.2. Apache Calcite¶
OmniSciDB uses Apache Calcite for frontline query parsing and cost-based optimization. Calcite runs as a separate process and communicates with the server using an Apache Thrift External API. Calcite returns an optimized relational algebra tree serialized via JSON. The serialized JSON string is passed to the RelAlgExecutor for execution.
Note
Calcite is used only for DML statements. For DDL statements, OmniSciDB uses a lightweight Bison-based parser.
7.1.3. Relational Algebra Executor¶
The RelAlgExecutor manages the execution of a relational algebra query. The input to the RelAlgExecutor is a relational algebra tree serialized in a JSON string, or an already deserialized tree via RelAlgDagBuilder. The RelAlgExecutor converts the RA DAG into a query plan, optimizes OmniSciDB specific query plans, translates each node in the query plan into an abstract syntax tree (AST) for code generation, and finally creates a work unit for each AST and passing the work unit to the Executor for kernel compilation and execution. While OmniSciDB attempts to consolidate queries to minimize the number of query steps (see doc:./optimization), some queries may have multiple intermediate steps. The RelAlgExecutor manages execution for each query step and stores the state of previous steps for use in later steps.
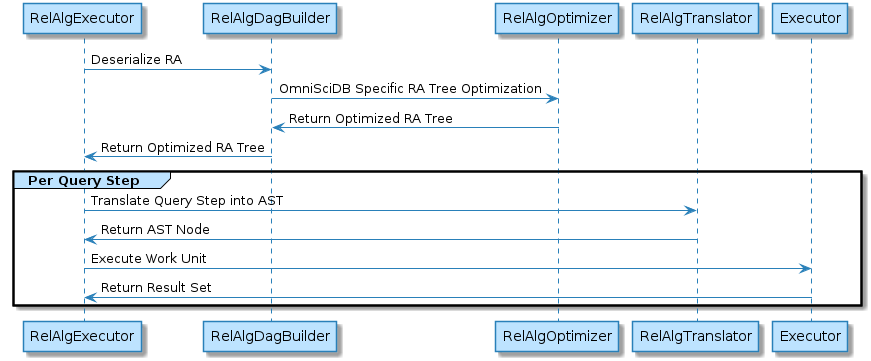
7.1.4. Relational Algebra Dag Builder and Optimizer¶
The RelAlgDagBuilder deserializes the JSON string containing the optimized relational algebra tree from Calcite. The builder creates a RelAlgNode object for each top-level relational algebra node. Each RelAlgNode is made up of Rex (relational algebra expression) nodes. The builder also manages OmniSciDB specific query optimizations (see DAG Builder / Optimizer). After optimization, each RA node in the DAG is a discrete unit of execution, typically referred to as a query step.
7.1.5. Relational Algebra Translator¶
Once an optimized relational algebra DAG has been assembled, each top-level RelAlgNode is executed. The RelAlgTranslator is the first step in node execution. To execute a query step, the RA node must be converted into an abstract syntax tree (AST). The AST drives code generation, building an execution kernel specified by the type of the RA node and its expressions. The input to the RelAlgTranslator is a RelAlgNode, and the output of the RelAlgTranslator is a set of Analyzer nodes specifying the inputs, outputs, filters, and expressions required for the query step.
7.1.6. Executor¶
The RelAlgExecutor packages the Analyzer nodes into a work unit and passes the work unit to the Executor for code generation and kernel execution. The executor manages generating machine code by walking the abstract syntax tree and building up an intermediate representation for the machine code. OmniSciDB uses LLVM for both the intermediate code representation (LLVMIR) and for converting the IR to machine code. Once machine code has been generated, the Executor manages the memory allocations, scheduling, and dispatch of the generated code. The executor returns a pointer to a ResultSet for each input work unit.